« PS:Embolie pulmonaire » : différence entre les versions
Aucun résumé des modifications |
|||
| (12 versions intermédiaires par 2 utilisateurs non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 8 : | Ligne 8 : | ||
[[File:Embolie pulmonaire.jpeg|750x660px|Embolie pulmonaire.jpeg]] | [[File:Embolie pulmonaire.jpeg|750x660px|Embolie pulmonaire.jpeg]] | ||
== Cas de l'embolie pulmonaire instable hémodynamiquement == | == Cas de l'embolie pulmonaire instable hémodynamiquement == | ||
*[[PS:HELP EP|Recours au groupe expert HELP-EP]] | |||
*AngioTDM si possible | |||
*Sinon ECMU cardio (cf critères d'IVD aigue) et ECMU 4 points (diagnostic positif) et ECMU pulmonaire (diagnostic différentiel) | |||
<br> | |||
== Probabilité clinique == | == Probabilité clinique == | ||
| Ligne 68 : | Ligne 70 : | ||
<span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblAuthors">Robert-Ebadi H;Mostaguir K;Hovens MM;Kare M;Versch. </span><span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblTitle" style="font-weight:bold">Assessing clinical probability of pulmonary embolism: prospective validation of the simplified Geneva score. </span><span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblSource">J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jul 8. doi: 10.1111/jth.13770.</span>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28688113?dopt=Abstract PMID: 28688113] | <span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblAuthors">Robert-Ebadi H;Mostaguir K;Hovens MM;Kare M;Versch. </span><span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblTitle" style="font-weight:bold">Assessing clinical probability of pulmonary embolism: prospective validation of the simplified Geneva score. </span><span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblSource">J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jul 8. doi: 10.1111/jth.13770.</span>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28688113?dopt=Abstract PMID: 28688113] | ||
=== règle PERC === | === règle PERC === | ||
| Ligne 101 : | Ligne 104 : | ||
Effect of the Pulmonary Embolism Rule-Out Criteria on Subsequent Thromboembolic Events Among Low-Risk Emergency Department Patients The PROPER Randomized Clinical Trial; Y.Freund and al, JAMA. 2018;319(6):559-566. [https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2672630 doi:10.1001/jama.2017.21904] | Effect of the Pulmonary Embolism Rule-Out Criteria on Subsequent Thromboembolic Events Among Low-Risk Emergency Department Patients The PROPER Randomized Clinical Trial; Y.Freund and al, JAMA. 2018;319(6):559-566. [https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2672630 doi:10.1001/jama.2017.21904] | ||
| |||
=== 4PEPS === | |||
{| style="width: 550px" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
score à 13 variables<br/> [https://peps.shinyapps.io/PEPS/ calculateur sur ce lien (en anglais)] | |||
| style="text-align: center" | | |||
|- | |||
| Age < 50 ans ou | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''-2''' | |||
|- | |||
| Age 50-64 ans | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''-1''' | |||
|- | |||
| insuffisance respiratoire chronique | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''-1''' | |||
|- | |||
| Frequence cardiaque <80 | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''-1''' | |||
|- | |||
| Douleur thoracique & dyspnée aigüe | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+1''' | |||
|- | |||
| Masculin | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+1''' | |||
|- | |||
| Traitement par oestrogène | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+2''' | |||
|- | |||
| Antécédant personnel de TVP | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+2''' | |||
|- | |||
| Syncope | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+2''' | |||
|- | |||
| Immobilisation dans les 4 semaines précédentes | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+2''' | |||
|- | |||
| SpO2< 95% | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+3''' | |||
|- | |||
| Douleur au mollet et / ou œdème unilatéral des membres inférieurs | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+3''' | |||
|- | |||
| L'embolie pulmonaire est le diagnostic le plus probable | |||
| style="text-align: center" | '''+5''' | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
Probabilité prétest clinique | |||
*Tres faible (<2%): Embolie pulmonaire exclue si 4PEPS<0 | |||
*Faible (2%-20%): Embolie pulmonaire exclue si 4PEPS=0-5 et D-dimer <1.0 μg/mL | |||
*Modérée (20%-65%): Embolie pulmonaire exclues si 4PEPS = 6-12 et D-dimer level <0.5 μg/mL ou <(age × 0.01) μg/mL | |||
*Elevée (>65%): Embolie pulmonaire exclue si 4PEPS>12 et AngioTDM pulmonaire normale | |||
| style="text-align: center" | | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
JAMA Cardiol. doi:[https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/2776853?utm_campaign=articlePDF&utm_medium=articlePDFlink&utm_source=articlePDF&utm_content=jamacardio.2021.0064 10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0064]<br/> Published online March 3, 2021. | |||
| style="text-align: center" | | |||
|} | |||
| |||
== Evaluation paraclinique == | == Evaluation paraclinique == | ||
| Ligne 130 : | Ligne 204 : | ||
=== AngioTDM pulmonaire === | === AngioTDM pulmonaire === | ||
== Evaluation de la gravité == | == Evaluation de la gravité == | ||
[[File:Ep nh2022.png|upright]] | |||
[https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.16815 Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Review Yonathan Freund,Fleur Cohen-Aubart,Ben Bloom PMID: 36194215 DOI: 10.1001/jama.2022.16815] | |||
=== Filière Ambulatoire === | === Filière Ambulatoire === | ||
| Ligne 139 : | Ligne 218 : | ||
=== Hospitalisation (conventionnelle versus SI) === | === Hospitalisation (conventionnelle versus SI) === | ||
* | * | ||
==== (Score PESI simplifié) a supprimer ? ==== | |||
==== (Score PESI simplifié) a supprimer ? ==== | |||
*dilatation des cavités droites + critere aigu | *dilatation des cavités droites + critere aigu | ||
** | ** | ||
==== Echographie Clinique en Médecine d'Urgence (pointe VD) ==== | ==== Echographie Clinique en Médecine d'Urgence (pointe VD) ==== | ||
** | * | ||
** | |||
==== BNP et Troponine ==== | ==== BNP et Troponine ==== | ||
** | * | ||
** | |||
==== AngioTDM ==== | ==== AngioTDM ==== | ||
== Traitement == | == Traitement == | ||
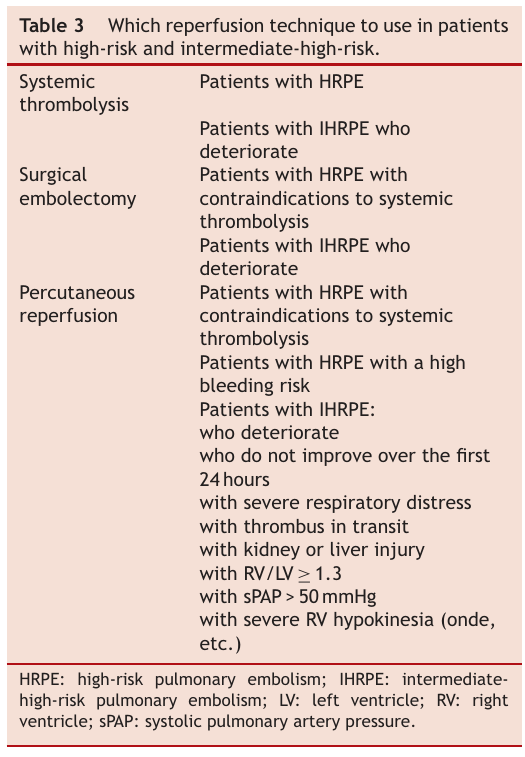
[[file:Risque_agravation_EP.png]] | |||
[[file:Evaluation_reperfusion_ep.jpg]] | |||
[[file:Reperfusion_EP_choix.png]] | |||
Réfrence: Reperfusion therapies in pulmonary embolism—state of the art and expert opinion: A position paper from the ‘‘Unité de Soins Intensifs de Cardiologie’’ group of the French Society of Cardiology 2020 [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2020.06.002 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2020.06.002]<br> | |||
=== Fibrinolyse === | === Fibrinolyse === | ||
Thrombolyse systémique par perfusion d'alteplase : 100 mg en 2 heures ou 0,6 mg/kg en 15 minutes,dose maximale 50 mg). | |||
=== Héparine === | === Héparine === | ||
| Ligne 168 : | Ligne 259 : | ||
Safety of the combination of PERC and YEARS rules in patients with low clinical probability of PE: a retrospective analysis of two large European cohorts. <span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblTitle" style="font-weight:bold">. </span><span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblSource">Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Jun 27. doi: 10.1111/acem.13508. </span><span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblArticleType" style="font-style:italic">(Original) </span>[https://plus.mcmaster.ca/EvidenceAlerts/R.aspx?U=31264&T=ABSTRACT+81845&L=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29947451?dopt=Abstract PMID: 29947451] | Safety of the combination of PERC and YEARS rules in patients with low clinical probability of PE: a retrospective analysis of two large European cohorts. <span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblTitle" style="font-weight:bold">. </span><span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblSource">Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Jun 27. doi: 10.1111/acem.13508. </span><span id="ctl00_ContentPlaceHolder_ctl00_lblArticleType" style="font-style:italic">(Original) </span>[https://plus.mcmaster.ca/EvidenceAlerts/R.aspx?U=31264&T=ABSTRACT+81845&L=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29947451?dopt=Abstract PMID: 29947451] | ||
Effect of a Diagnostic Strategy Using an Elevated and Age-Adjusted D-Dimer Threshold on Thromboembolic Events in Emergency Department Patients With Suspected Pulmonary Embolism: A Randomized Clinical Trial #REDIRECT [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34874418/ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34874418/] | |||
| | ||
== mise à jour: | == mise à jour: 10 février 2026 == | ||
[[Category:Protocoles de soins]] | [[Category:Protocoles de soins]] | ||
Dernière version du 10 février 2026 à 10:19
Fiche incomplète Ne pas utiliser
Algorithme sauf
- femme enceinte
- pédiatrie
- patient sous anticoagulation curative
- AngioTDM pulmonaire contre indiquée (allergie, insuffiance rénale..)
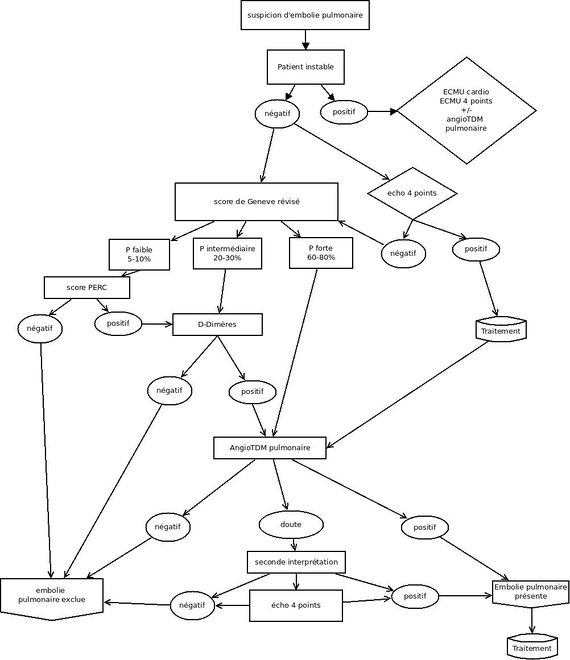
Cas de l'embolie pulmonaire instable hémodynamiquement
- AngioTDM si possible
- Sinon ECMU cardio (cf critères d'IVD aigue) et ECMU 4 points (diagnostic positif) et ECMU pulmonaire (diagnostic différentiel)
Probabilité clinique
score de Genève
| age > 65 ans | +1 |
| ATCD de TVP et/ou EP | +1 |
| Immobilisation ou chirurgie < 4 semaines | +1 |
| Cancer actif (ou résolu < 1 an) | +1 |
| Douleur jambe unilatérale | +1 |
| Hémoptysies | +1 |
| Fc: 75/94 bpm | +1 |
| Fc >= 95 | +2 |
| Douleur à la palpation et oedeme unilatéral de la jambe | +1 |
| |
probabilité prétest
- probabilité clinique faible => probabilité prétest < 10%
- probabilité clinique intermédiaire => probabilité prétest = 20-40%
- probabilité clinique forte => probabilité prétest = 60-80%
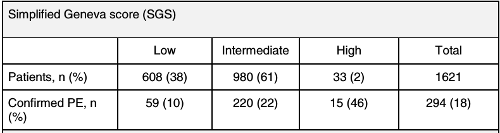
Robert-Ebadi H;Mostaguir K;Hovens MM;Kare M;Versch. Assessing clinical probability of pulmonary embolism: prospective validation of the simplified Geneva score. J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jul 8. doi: 10.1111/jth.13770.PMID: 28688113
règle PERC
| age > 50 ans | +1 |
| Fc > 100/mn | +1 |
| SaO2 en air ambiant <95% | +1 |
| Oedème de jambe unilateral | +1 |
| Hémoptysie | +1 |
| Chirurgie ou traumatisme de moins de 4 semaines | +1 |
| ATCD de TVP ou EP | +1 |
| Traitement hormonal (oestrogene) | +1 |
| si score = 0, probabilité d'embolie pulmonaire <2% | |
Effect of the Pulmonary Embolism Rule-Out Criteria on Subsequent Thromboembolic Events Among Low-Risk Emergency Department Patients The PROPER Randomized Clinical Trial; Y.Freund and al, JAMA. 2018;319(6):559-566. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.21904
4PEPS
|
score à 13 variables |
|
| Age < 50 ans ou | -2 |
| Age 50-64 ans | -1 |
| insuffisance respiratoire chronique | -1 |
| Frequence cardiaque <80 | -1 |
| Douleur thoracique & dyspnée aigüe | +1 |
| Masculin | +1 |
| Traitement par oestrogène | +2 |
| Antécédant personnel de TVP | +2 |
| Syncope | +2 |
| Immobilisation dans les 4 semaines précédentes | +2 |
| SpO2< 95% | +3 |
| Douleur au mollet et / ou œdème unilatéral des membres inférieurs | +3 |
| L'embolie pulmonaire est le diagnostic le plus probable | +5 |
|
Probabilité prétest clinique
|
|
|
JAMA Cardiol. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0064 |
Evaluation paraclinique
D-Dimères
Les D-dimères ne peuvent s'interpréter qu'après détermination de la probabilité pré-test grace à une règle clinique type Genève
- Si la probabilité pré-test est haute
- ne pas utiliser les D-Dimères
- Si la probabilité pré-test est intermédiaire
- un dosage de D-Dimières inférieurs à 500 ng/ml exclu le diagnostic
- Si la probablité pré-test est basse et la règle PERC >0
- un dosage des D-Dimères inférieurs à 1000 ng/ml exclu le diagnostic
D-dimer Interval Likelihood Ratios for Pulmonary Embolism: Acad Emerg Med. 2017 Jul;24(7):832-837. doi: 10.1111/acem.13191
Echographie clinique en médecine d'urgence (ECMU) multi-organe
si un des points suivants est présent chez les patients ayant un score de Wells>4 ou D-Dimeres >500 ng/ml
- ≥ 1 infarctus subpleural à l'échographie pulmonaire
- dilatation aigue du ventricule droit ou présence d'un thrombus intracavitaire droit à l'échographie cardiaque
- présence d'un test de compression 4 points positifs à l'échographie veineuse des membres inférieurs
le diagnostic d'embolie pulmonaire est posée. (Rapport de Vraisemblance positif = 6.5)
AngioTDM pulmonaire
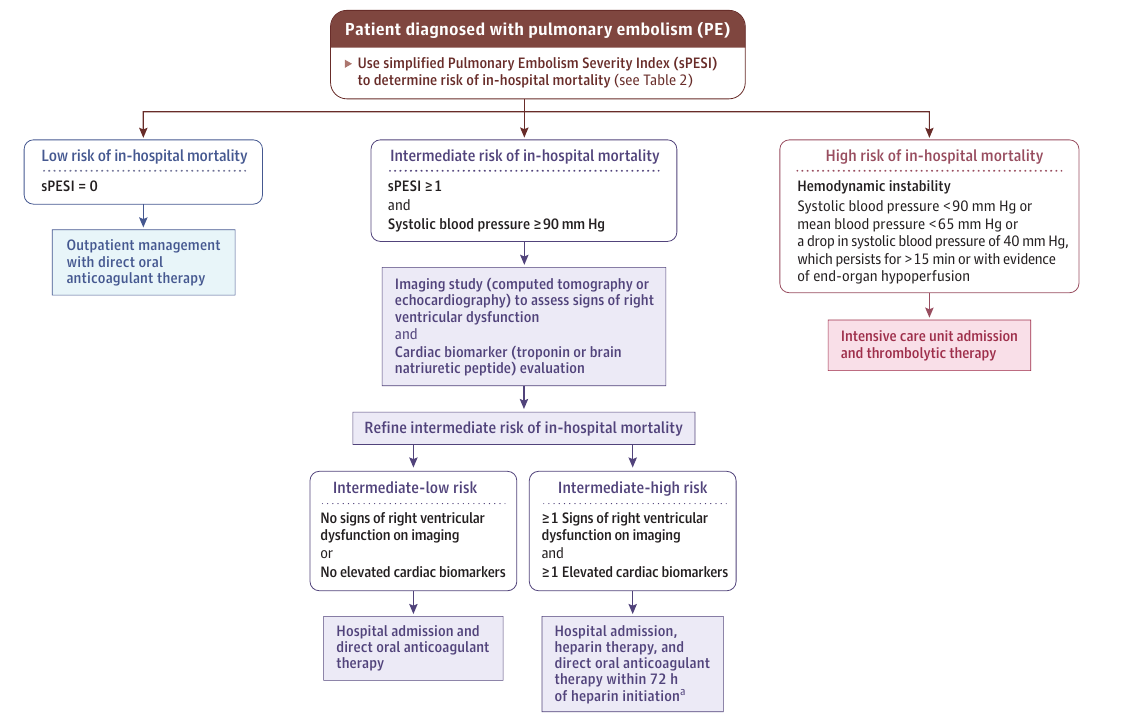
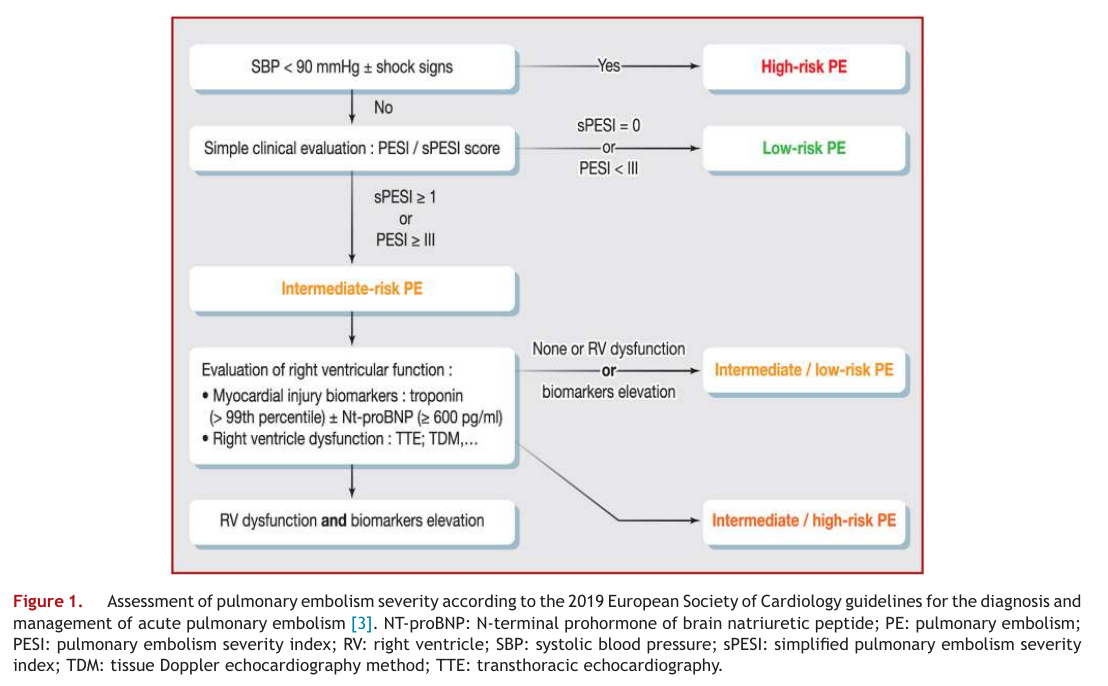
Evaluation de la gravité
Filière Ambulatoire
- score HESTIA
Hospitalisation (conventionnelle versus SI)
(Score PESI simplifié) a supprimer ?
- dilatation des cavités droites + critere aigu
Echographie Clinique en Médecine d'Urgence (pointe VD)
BNP et Troponine
AngioTDM
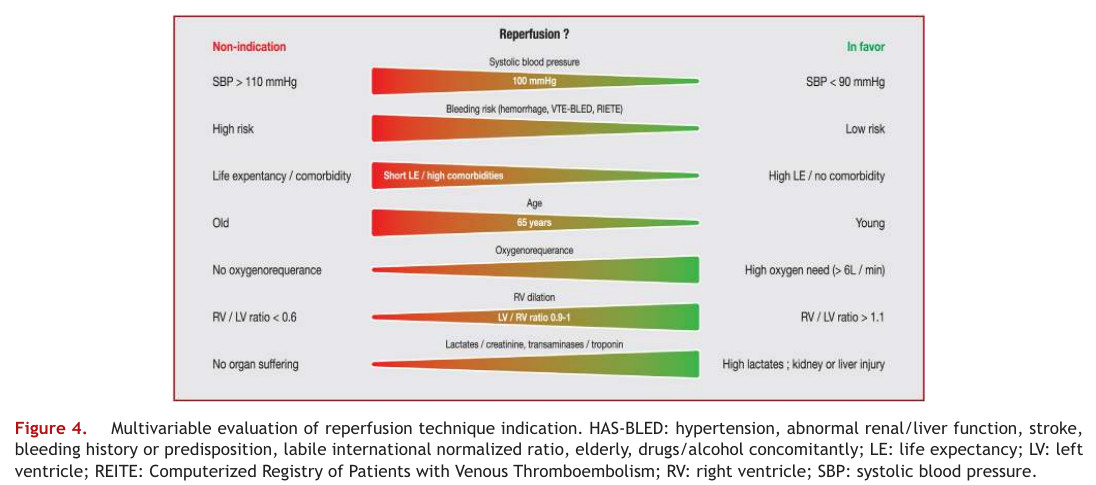
Traitement
Réfrence: Reperfusion therapies in pulmonary embolism—state of the art and expert opinion: A position paper from the ‘‘Unité de Soins Intensifs de Cardiologie’’ group of the French Society of Cardiology 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2020.06.002
Fibrinolyse
Thrombolyse systémique par perfusion d'alteplase : 100 mg en 2 heures ou 0,6 mg/kg en 15 minutes,dose maximale 50 mg).
Héparine
AOD
AVK
Bibiographie
Optimal Strategies for the Diagnosis of Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Health Technology Assessment. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH). 2018 Jan:1-438. (Systematic Review)
Safety of the combination of PERC and YEARS rules in patients with low clinical probability of PE: a retrospective analysis of two large European cohorts. . Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Jun 27. doi: 10.1111/acem.13508. (Original) PMID: 29947451
Effect of a Diagnostic Strategy Using an Elevated and Age-Adjusted D-Dimer Threshold on Thromboembolic Events in Emergency Department Patients With Suspected Pulmonary Embolism: A Randomized Clinical Trial #REDIRECT https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34874418/